By Kylie Conway
•
October 29, 2025
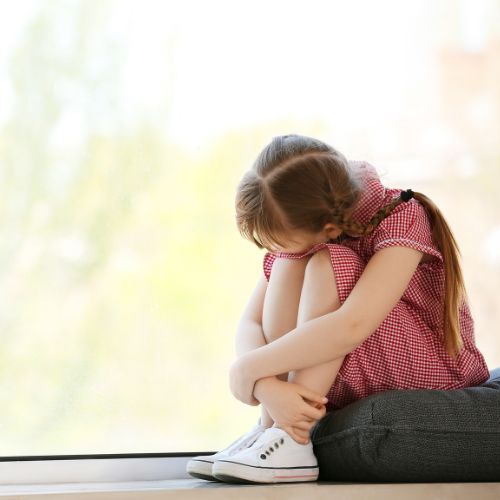
Understanding Daytime Wetting in Children: The “Why” Behind It Daytime bladder accidents, or daytime wetting, are surprisingly common in childhood. While many parents worry that something is “wrong” with their child, the truth is that bladder control is a complex process involving the bladder, pelvic floor muscles, bowel, nervous system, and even emotions. When one part of this system is under pressure, immature, or not communicating well with the others, wetting can occur. How Common Is Daytime Wetting? Research shows that daytime wetting is more frequent than many parents realise: Around 10% of children at age 5–6 experience daytime wetting. By age 7, prevalence drops to about 5%. At age 9, around 2–3% of children are still affected. This means that while most children develop bladder control naturally, a significant number need extra support to achieve dryness. 1. The Developing Bladder-Brain Connection To stay dry during the day, children need to: Feel the bladder filling (sensory signal) Recognise that signal as “I need to go” Respond quickly by activating the pelvic floor and then relaxing it at the right time on the toilet. In some children, this communication loop between the bladder and brain matures later. This can mean: They don’t notice bladder fullness until the last moment. This may result as a sudden strong urge and may present as them “dancing” or holding themselves. Their bladder muscle (the detrusor) may contract involuntarily, pushing urine out before they are ready. This explains why children often appear “fine one moment, bursting the next.” 2. Overactive or “Irritable” Bladder Sometimes the bladder itself is the driver. An overactive detrusor muscle contracts too frequently, leading to urgency and accidents. This may be linked to: Drinking bladder irritants (soft drink, caffeine, artificial colours/flavours). Post-bladder infection sensitivity. Constipation pressing on the bladder and reducing its capacity. Children with overactive bladder often experience frequent small wees, urgency, and may show classic “holding manoeuvres” like squatting or crossing their legs. 3. Constipation and the Bladder-Bowel Link Up to 30–50% of children with daytime wetting also have constipation. A constipated bowel takes up valuable space in the pelvis, which can reduce the bladder’s storage capacity. Treating constipation is often the first and most effective step in resolving bladder problems. 4. Pelvic Floor Muscle Dysfunction The pelvic floor muscles must hold on at the right time and relax at the right time. If these muscles are too tight or discoordinated, the child may not empty properly, which can lead to dribbling, urgency, or urinary tract infections. This is where pelvic health physiotherapists use age-appropriate education and biofeedback to help children learn how their muscles work. 5. Neurodivergence and Bladder Control Children who are autistic, ADHD, or have sensory processing differences often experience higher rates of bladder and bowel challenges. Studies suggest that children with ADHD are 2–3 times more likely to experience incontinence compared to neurotypical peers. The pathophysiology here can involve: Altered sensory processing: bladder fullness may not be felt until very late. Executive function differences: difficulty shifting attention from play or schoolwork to respond to body cues. Anxiety or rigidity: avoiding toilets outside the home due to sound, smell, or sensory overwhelm. Medication effects: some ADHD medications may influence urinary frequency or urgency. The key message: the bladder is working within the unique way that child’s nervous system processes information. 6. Behavioural and Emotional Factors Stressful life events, school changes, bullying, or family transitions can all impact bladder control. In these cases, the child’s nervous system may be on “high alert,” influencing bladder muscle activity and pelvic floor responses. Wetting in these cases is not deliberate — it’s the body’s way of responding to stress. How Treatment Helps When we understand why wetting occurs, treatment can be tailored to the child’s needs. A collaborative approach between pelvic health physiotherapists, GPs, and sometimes paediatricians may include: Bladder training: establishing healthy toileting routines. Constipation management: diet, fluids, or medication if required. Pelvic floor awareness: playful, child-friendly exercises to improve coordination. Behavioural strategies: rewards, charts, or visual schedules. Environmental changes: school toileting plans, sensory adjustments. With the right support, most children improve significantly — and many achieve dryness within months. The Takeaway Daytime wetting is rarely about laziness or misbehaviour. It is the result of interacting bladder, bowel, muscle, and brain factors – all of which can be supported with the right guidance. If your child experiences daytime wetting, know that you are not alone, and that early intervention can help prevent ongoing issues with confidence, social participation, and urinary health. Our team at Pelvic Health Melbourne works closely with families, GPs, and other health professionals to provide child-friendly, evidence-based care.